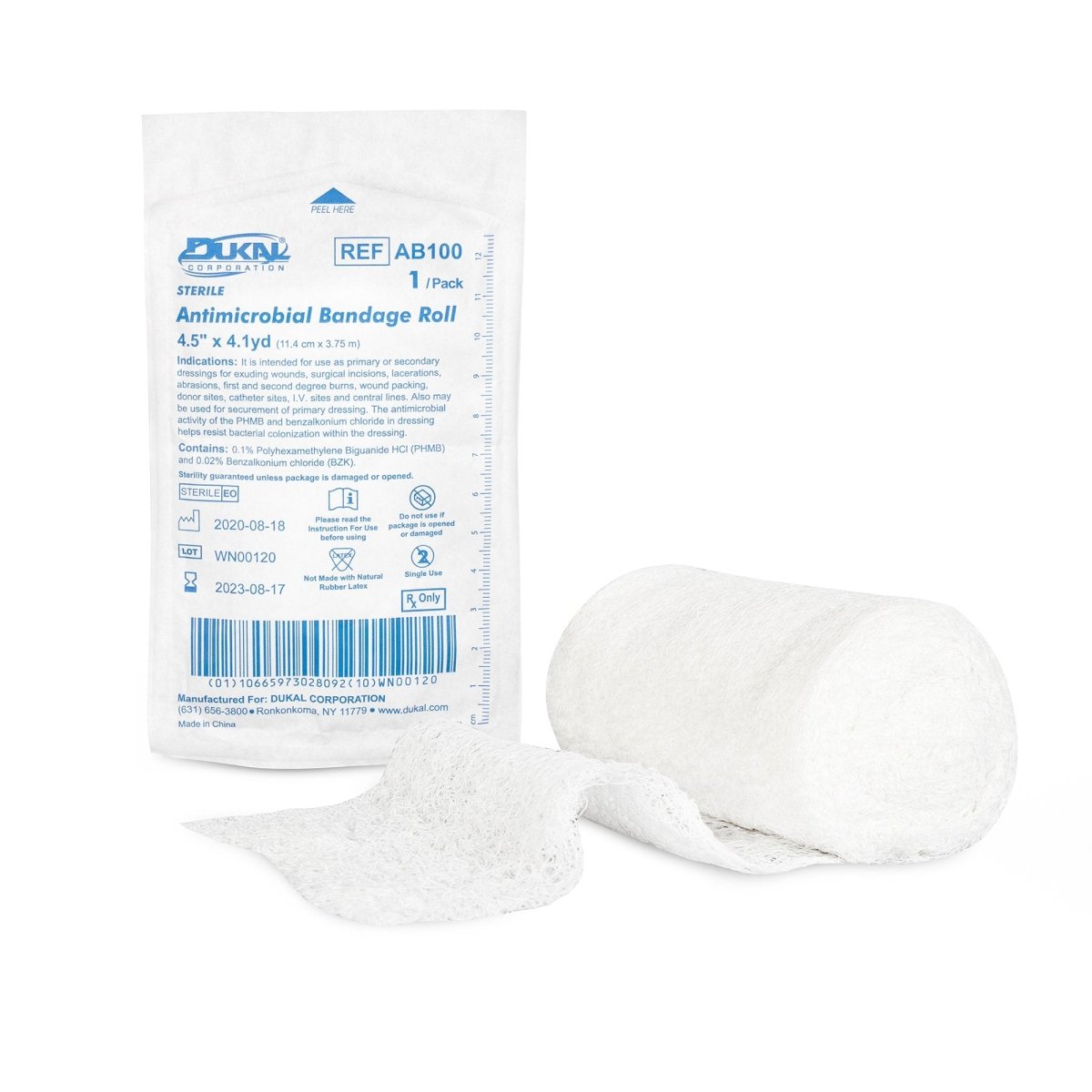
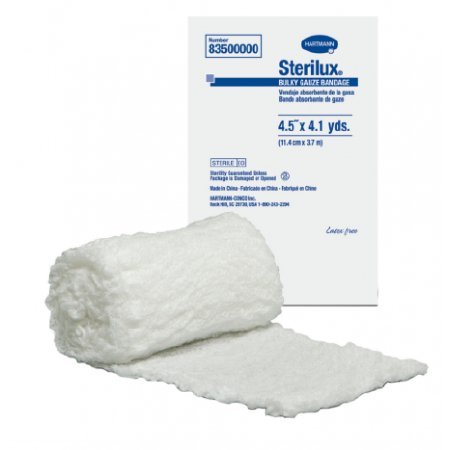
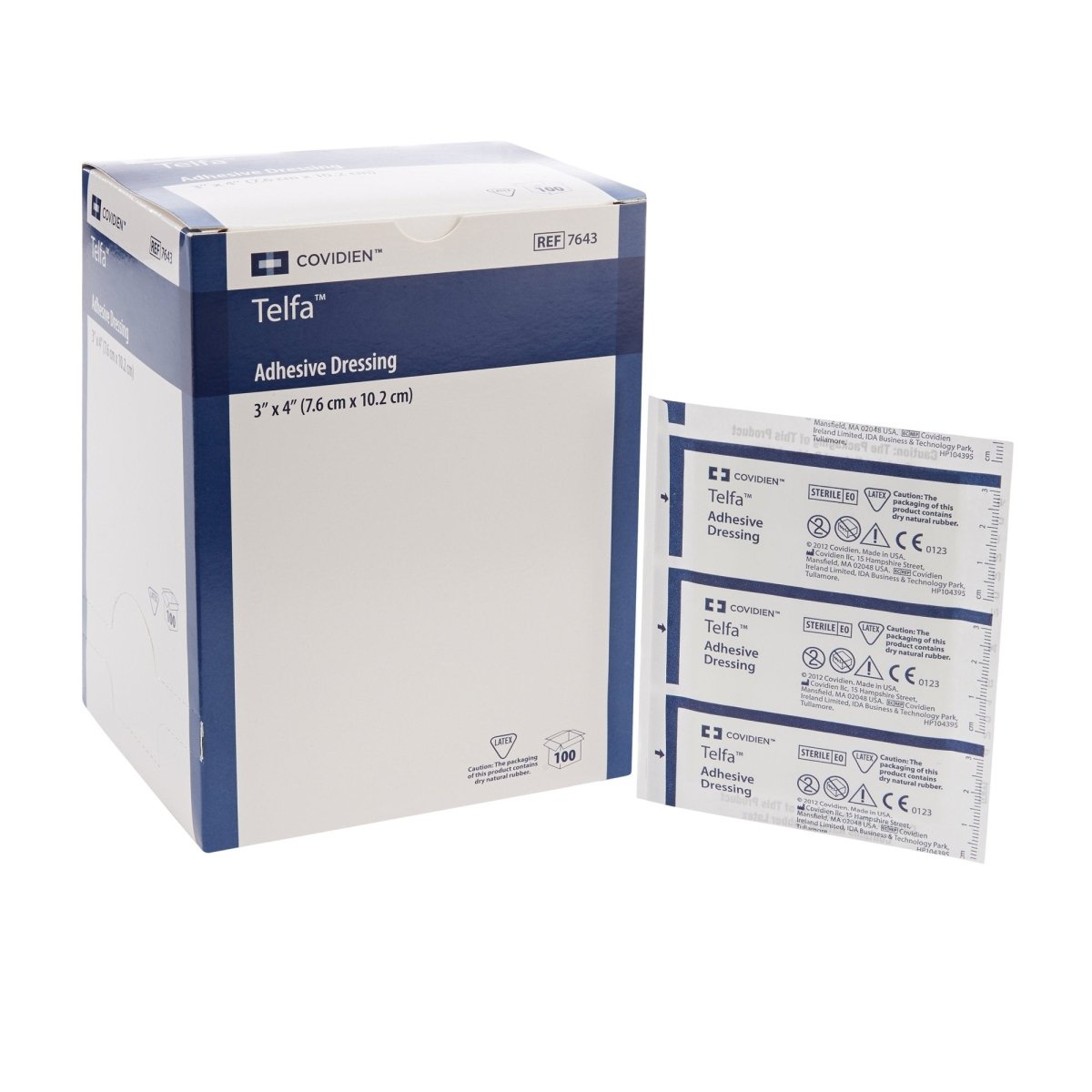
Shop our Selection of Wound Care Dressings and Gauze
Wound care dressings and gauze are essential components of wound care management. They're used to help heal minor cuts and scrapes, as well as larger, more serious wounds. Browse our selection of dressing and gauze bandages online with discreet shipping.
- Dressings provide a barrier between the wound and the environment, helping to reduce the risk of infection.
- Gauze pads are used to absorb excess fluid from a wound to keep it clean and dry.
- Gauze rolls, also known as bandages, are used to hold dressings in place and provide support to the wound area.
- Various types of wound care dressings are available, including antimicrobial, hydrocolloid, foam, and adhesive dressings.
Choosing the right dressing or gauze for your wound helps prevent infection and ensure the best possible healing process. Make sure to follow the manufacturers instructions for use and change the dressing regularly.
Frequently Asked Questions about Dressings & Gauze
Do you still have questions about Dressings & Gauze?
If we still haven't answered your question, you can contact us by phone or email and we will get back to you as soon as possible.