Wound Care FAQ
Frequent Questions about Wound Care Products
Step 1. Wash your hands with soap and water before tending to the wound. This will help prevent infection
Step 2. Stop the bleeding by applying pressure to the wound with a clean and dry cloth or bandage. Also move the wound so it is above the heart to slow the bleeding.
Step 3. Use running water to clean the wound. Try to flush any dirt or debris to prevent infection.
Step 4. If the would is minor apply antibacterial ointment.
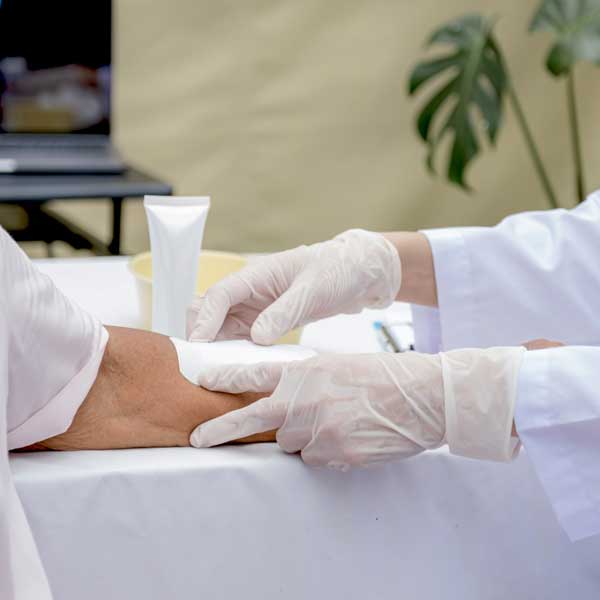
Step 5. Protect the wound by covering with a sterile bandage.
Step 6. Change dressing of would every 24 hours.
Step 7. Be on the look out for pain, odor, and discharge.
Proper wound care includes keeping the wound clean and dry.
Medical tape, Gauze sponges, non-woven sponges, alcohol pads, face masks, bandages and dressings, medical gloves, gauze rolls, cotton tip applicators, and cotton balls, antibacterial ointment.
Wound healing occurs in four phases. Hemostasis, inflammation, proliferation, and remodeling.
There are several types of wounds. penetrating wounds, puncture wounds, surgical wounds and incisions. There are also thermal, chemical or electric burns, bites and stings, gunshot wounds, or other high velocity projectiles that can penetrate the body, blunt force trauma, abrasions, lacerations, and skin tears.
Still have a Question?
If we still haven't answered your questions, you can contact us below and we will be glad to assist you. Our goal is your satisfaction.